Ohm's Law: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The standard disclaimers pertaining to the information contained on this wiki page are listed [[Disclaimers | here.]]<br/> | The standard disclaimers pertaining to the information contained on this wiki page are listed [[Disclaimers | here.]]<br/> | ||
'''THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION AND IS NOT COMPLETE AND HAS NOT BEEN CHECKED FOR ERRORS YET!!'''<br/> | '''THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION AND IS NOT COMPLETE AND HAS NOT BEEN CHECKED FOR ERRORS YET!!'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Ohm's Law== | ==Ohm's Law== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
:::'''V=IR'''<br/> | :::'''V=IR'''<br/> | ||
:::'''Voltage = Current x Resistance'''<br/> | :::'''Voltage = Current x Resistance'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Ohm's Law Diagram== | ==Ohm's Law Diagram== | ||
The following diagram shows the relationship between the various electrical properties.<br/> | The following diagram shows the relationship between the various electrical properties.<br/> | ||
[[File:Ohms-law.jpg|300px]]<br/> | [[File:Ohms-law.jpg|300px]]<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Voltage '''(V)'''== | ==Voltage '''(V)'''== | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage Voltage] is measured in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volt volts] (V). Voltage is a measure of the electric potential difference between two points.<br/> | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage Voltage] is measured in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volt volts] (V). Voltage is a measure of the electric potential difference between two points.<br/> | ||
There are two basic type of voltage:<br/> | There are two basic type of voltage:<br/> | ||
===AC Voltage=== | |||
*'''AC''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alternating_current Alternating Current] | *'''AC''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alternating_current Alternating Current] | ||
**Example: | **Example: | ||
***The voltage of a typical wall power outlet in the United States is 120 volts AC (VAC). | ***The voltage of a typical wall power outlet in the United States is 120 volts AC (VAC). | ||
===DC Voltage=== | |||
*'''DC''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_current Direct Current] | *'''DC''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_current Direct Current] | ||
**Example: | **Example: | ||
***The voltage of a typical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nickel%E2%80%93metal_hydride_battery NiMh AA battery] is 1.25 volts DC (VDC). | ***The voltage of a typical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nickel%E2%80%93metal_hydride_battery NiMh AA battery] is 1.25 volts DC (VDC). | ||
***Many Integrated Circuits require 5 volts DC (VDC) to power them. | ***Many Integrated Circuits require 5 volts DC (VDC) to power them. | ||
===Voltage Formulas=== | |||
**V=IR | **'''V=IR''' | ||
**V=√<span style="text-decoration: overline">PR</span> | **'''V=√<span style="text-decoration: overline">PR</span>''' | ||
**V=P/I | **'''V=P/I'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Current '''(I)'''== | ==Current '''(I)'''== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 39: | ||
**A typical LED draws 20 milliamps (0.02A or 20mA). | **A typical LED draws 20 milliamps (0.02A or 20mA). | ||
**A typical string of 100 count incandescent lights draws 0.33A. | **A typical string of 100 count incandescent lights draws 0.33A. | ||
===Current Formulas=== | |||
**I=V/R | **'''I=V/R''' | ||
**I=P/V | **'''I=P/V''' | ||
**I=√<span style="text-decoration: overline">P</span>/R | **'''I=√<span style="text-decoration: overline">P</span>/R'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Resistance '''(R)'''== | ==Resistance '''(R)'''== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 49: | ||
*Example: | *Example: | ||
**A common current limiting resistor for driving optoisolators is 680 ohms (Ω). | **A common current limiting resistor for driving optoisolators is 680 ohms (Ω). | ||
===Resistance Formulas=== | |||
**R=V/I | **'''R=V/I''' | ||
**R=V²/P | **'''R=V²/P''' | ||
**R=P/I² | **'''R=P/I²'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Power '''(P)'''== | ==Power '''(P)'''== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 62: | ||
*Example: | *Example: | ||
**A common table lamp is 100 watts (100w). | **A common table lamp is 100 watts (100w). | ||
===Power Formulas=== | |||
**'''P=VI''' | **'''P=VI''' | ||
**'''P=I²R''' | **'''P=I²R''' | ||
**'''P=V²/R''' | **'''P=V²/R'''<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==LED Calculator== | ==LED Calculator== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 75: | ||
===Array of LEDs=== | ===Array of LEDs=== | ||
[http://led.linear1.org/led.wiz LED Calculator] for an array of LEDs.<br/> | [http://led.linear1.org/led.wiz LED Calculator] for an array of LEDs.<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
==Pixel Voltage Drop Calculator== | ==Pixel Voltage Drop Calculator== | ||
Due to the high current used by pixels and the small guage wires used by many people, there can be issues due to voltage drops caused by the wire resistance.<br/> | Due to the high current used by pixels and the small guage wires used by many people, there can be issues due to voltage drops caused by the wire resistance.<br/> | ||
[http://doityourselfchristmas.com/forums/showthread.php?20242-New-tools-for-estimating-pixels-string-voltage-drops Thread]<br/> | [http://doityourselfchristmas.com/forums/showthread.php?20242-New-tools-for-estimating-pixels-string-voltage-drops Thread]<br/> | ||
[http://blinkyflashy.info/calcs/pixpower.php Voltage Drop Calculator] | [http://blinkyflashy.info/calcs/pixpower.php Voltage Drop Calculator]<br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
[[Category:DIYC Index]] | [[Category:DIYC Index]] | ||
[[Category:General Info]] | [[Category:General Info]] | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 28 October 2012
Disclaimers
The standard disclaimers pertaining to the information contained on this wiki page are listed here.
THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION AND IS NOT COMPLETE AND HAS NOT BEEN CHECKED FOR ERRORS YET!!
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is a formula that relates the basic electrical properties of Voltage, Current and Resistance. These properties can be measured with a multimeter.
The common formula for Ohm's Law is:
- V=IR
- Voltage = Current x Resistance
- V=IR
Ohm's Law Diagram
The following diagram shows the relationship between the various electrical properties.
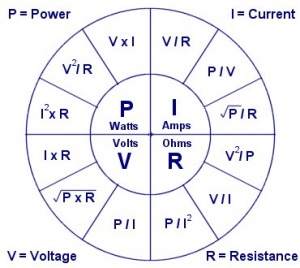
Voltage (V)
Voltage is measured in volts (V). Voltage is a measure of the electric potential difference between two points.
There are two basic type of voltage:
AC Voltage
- AC Alternating Current
- Example:
- The voltage of a typical wall power outlet in the United States is 120 volts AC (VAC).
- Example:
DC Voltage
- DC Direct Current
- Example:
- The voltage of a typical NiMh AA battery is 1.25 volts DC (VDC).
- Many Integrated Circuits require 5 volts DC (VDC) to power them.
- Example:
Voltage Formulas
- V=IR
- V=√PR
- V=P/I
Current (I)
Current is measured in amps (A). Current is a measure of the flow of electric charge. Current is often measured in milliamps (ma) in many electronic circuits. A milliamp is one thousandth of an amp (0.001A).
- Example:
- A typical LED draws 20 milliamps (0.02A or 20mA).
- A typical string of 100 count incandescent lights draws 0.33A.
Current Formulas
- I=V/R
- I=P/V
- I=√P/R
Resistance (R)
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance is a measure of the opposition to the passage of an electric current through a circuit component. Resistors are the most common form of resistance in circuits.
- Example:
- A common current limiting resistor for driving optoisolators is 680 ohms (Ω).
Resistance Formulas
- R=V/I
- R=V²/P
- R=P/I²
Power (P)
Power is measured in watts (W). Power is a measure of the rate of doing work.
The common formula for Power is:
- P=VI
- Power=Voltage x Current
- P=VI
- Example:
- A common table lamp is 100 watts (100w).
Power Formulas
- P=VI
- P=I²R
- P=V²/R
LED Calculator
By using Ohm's Law you can calculate the current limiting resistor needed to include in a circuit with a LED.
Single LED
LED Calculator for 1 LED.
Array of LEDs
LED Calculator for an array of LEDs.
Pixel Voltage Drop Calculator
Due to the high current used by pixels and the small guage wires used by many people, there can be issues due to voltage drops caused by the wire resistance.
Thread
Voltage Drop Calculator