Choosing a Pixel Voltage: 5V vs 12V: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
[[Things You Will Need To Get Started With Pixels]] <br> | [[Things You Will Need To Get Started With Pixels]] <br> | ||
[[Pixel Wiring Colors]] <br> | [[Pixel Wiring Colors]] <br> | ||
[[Power Supplies]] | |||
[[Category:RGB]] | [[Category:RGB]] | ||
[[Category:DIYC Index]] | [[Category:DIYC Index]] | ||
[[Category:Pixel]] | [[Category:Pixel]] | ||
Revision as of 19:54, 27 June 2013
General
Disclaimers
The standard disclaimers pertaining to the information contained on this wiki page are listed here.
THIS BOARD IS STILL IN DEVELOPMENT AND SUBJECT TO CHANGE.
THIS WIKI PAGE IS NOT COMPLETE YET.
How RGB LEDs work
Current Limiting Resistors
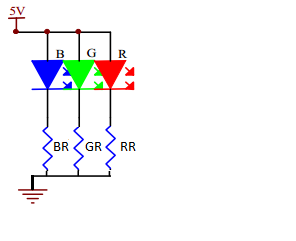
- What resistor would you use with a 5VDC power supply and a Blue 8mm LED with a VF of 3.0V?
First you need to calculate the voltage that the resistor needs to drop. That is equal to
VDrop=VPowerSupply - VF=5-3=2V
The table below recommends a current I of 20 ma for a 8mm LED. The formula for resistance gives us:
R=V/I=2/0.02=100Ω Generally you choose a resistor for that value or the next higher standard resistor value.
To calculate the wattage resistor needed you use the formula for Power:
P=VI=(2)(0.02)= 0.04W. You would use the next standard size up resistor, 1/8 W.
| Typical 8mm RGB LED Properties | |||
| Color | Forward Voltage VF @ 20ma | ||
| Minimum | Typical | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 1.8V | 2.0V | 2.2V |
| Green | 3.0V | 3.2V | 3.4V |
| Blue | 3.0V | 3.1V | 3.4V |
Different Voltage Configurations
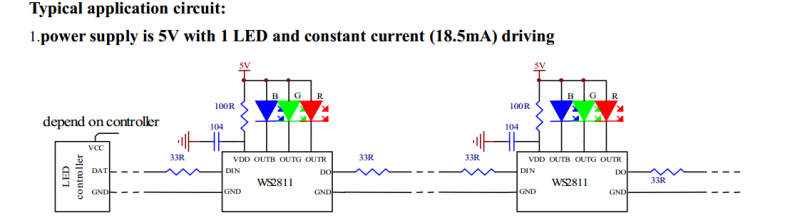
5V Power and 1 RGB LED
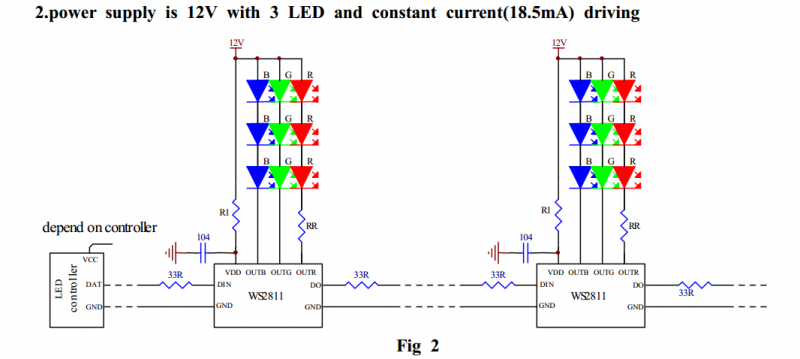
12V Power and 3 RGB LEDs
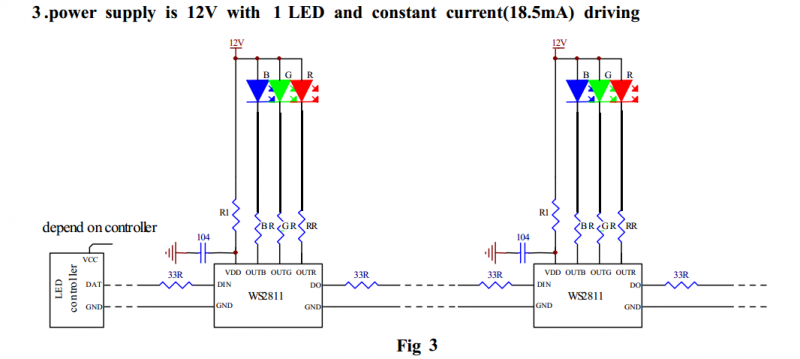
12V Power and 1 RGB LED
Related Links
Different Styles of Pixels
Controllers
Dumb RGB or Intelligent Pixels??
Things You Will Need To Get Started With Pixels
Pixel Wiring Colors
Power Supplies