Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is a formula that relates the basic electrical properties. These properties can be measured with a multimeter. The common formula for Ohm's Law is:
- V=IR
- Voltage = Current x Resistance
- V=IR
Ohm's Law Diagram
The following diagram shows the relationship between the various electrical properties.
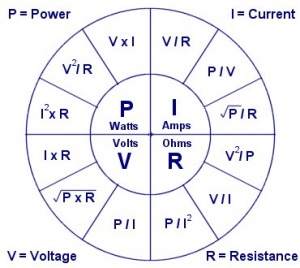
Voltage (V)
Voltage is measured in volts (V). Voltage is a measure of the electric potential difference between two points. There are two basic type of voltage:
- AC Alternating Current
- Example:
- The voltage of a typical wall power outlet in the United States is 120 volts AC (VAC).
- Example:
- DC Direct Current
- Example:
- The voltage of a typical NiMh AA battery is 1.25 volts DC (VDC).
- Many Integrated Circuits require 5 volts DC (VDC) to power them.
- Example:
Current (I)
Current is measured in amps (A). Current is a measure of the flow of electric charge. Current is often measured in milliamps (ma) in many electronic circuits. A milliamp is one thousandth of an amp (0.001A).
- Example:
- A typical LED draws 20 milliamps (0.02A or 20mA).
Resistance (R)
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance is a measure of the opposition to the passage of an electric current through a circuit component. Resistors are the most common form of resistance in circuits.
- Example:
- A common current limiting resistor for driving optoisolators is 680 ohms (Ω).
Power (P)
Power is measured in watts (W). Electric power is a measure of the rate of doing work. The common formula for Power is:
- P=VI
- Power=Voltage x Current
- P=VI
- Example:
- A common table lamp is 100 watts (100w).
LED Calculator
Use these calculators to calculate the resistor needed to include in a circuit with a LED.
Single LED
LED Calculator for 1 LED.
Array of LEDs
LED Calculator for an array of LEDs.