Renard SS8 Controller Board: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
::'''Jumpers''' | ::'''Jumpers''' | ||
:::* '''JP1''' – RS232 signal ground. Install a shunt (jumper) on JP1 when receiving RS232 data. | :::* '''JP1''' – RS232 signal ground. Install a shunt (jumper) on JP1 when receiving RS232 data. | ||
:::* '''JP2''' – 120 ohm termination resistor enable. Normally a shunt will be installed on JP2. Remove the shunt if you are experiencing problems with incoming data. | :::* '''JP2''' – 120 ohm termination resistor enable. Normally a shunt will be installed on JP2 when receiving RS485 data. Remove the shunt if you are experiencing problems with incoming data. | ||
:::* '''JP3''' – Diagnostic LEDs enable. Install a shunt on JP3 to allow the Diagnostic LEDs to function. During normal operation, you can remove the shunt with no negative impact on board operation. | :::* '''JP3''' – Diagnostic LEDs enable. Install a shunt on JP3 to allow the Diagnostic LEDs to function. During normal operation, you can remove the shunt with no negative impact on board operation. | ||
| Line 246: | Line 246: | ||
:::* The total number of Renard boards that can be connected together depends on the event period and the baud rate being used. More information on the total number of channels capable with Renard systems can be found here [[Renard#Number of Circuits (Channels) | here.]] | :::* The total number of Renard boards that can be connected together depends on the event period and the baud rate being used. More information on the total number of channels capable with Renard systems can be found here [[Renard#Number of Circuits (Channels) | here.]] | ||
=='''Configuring the jumpers on Renard SS boards'''== | |||
:'''JP1 & JP2 Configuraton''' | |||
:The configuration of JP1 and JP2 depends on the type of communication being used: | |||
<br> | |||
::'''RS-232 Communication (direct connect to PC)''' | |||
:::*'''JP1''' installed | |||
:::*'''JP2''' not installed | |||
:::Reminder: This only applies to the first Renard SS board connected to the PC. The output of a Renard SS board to the next board is RS-485. | |||
<br> | |||
::'''RS-485 Communication (output of a Renard board or output from a RS-485 adapter/converter)''' | |||
:::*'''JP1''' not installed | |||
:::*'''JP2''' installed (try removing if data communication issues are encountered) | |||
<br> | |||
:'''JP3 Configuraton''' | |||
::*Installed when running the Diagnostics Firmware | |||
::*Normally not installed when running the Operational Firmware. But can be left installed if you don’t mind seeing the on-board LEDs responding with the associated channels. | |||
Revision as of 23:16, 26 November 2011
Introduction
- The Renard SS8 is a PIC microcontroller based Christmas light controller with 8 solid state relay circuits incorporated into the board. The board design is based on the PIC-based 8-port dimmer concept originally developed by Phil Short. Information on the original concept can be viewed here. Generic information pertaining to current Renard designs (including maximum channel count) can be found on the Renard wiki page.
- The Renard Standardized Series (SS) controllers are part of a design effort to standardize the board layouts for Renard based systems and to establish a standardized list of components to use in Renard designs. Some of the goals of the Renard SS design effort were:
- Completely self-contained controller board. All that is needed to start using the board is a data input and an AC power source. No external DC voltage supply or externally generated ZC is needed and there is no need for an off-board neutral bar.
- Common part list used for all boards. There are no special parts for any individual board, all the boards use the same components. The only thing different is the quantity used on each board.
- Common component layout on the board. With only a few exceptions, all the components on the boards are laid out in the same fashion.
- On-board LEDs for full support of Renard diagnostics firmware.
- Easier for a new member to build. By removing extra options from the board, now a member can just order the parts from the BOM and will be able to build the board without having to figure out which options/parts apply to their configuration.
- Easier to support. By having all the boards using the same parts and having the same component layout, it will be easier to provide support to DIYC members when they have problems or ask questions.
- Complete documentation. In the past, boards were created, designed, produced and distributed without much documentation to support them. Documentation was an afterthought and was slow to catch up, some never did or is hard to understand for new members. In the Renard SS design effort, the documentation was created at the same time as the boards so that when the boards were ready for release, the documentation was also ready.
Disclaimers
- The standard disclaimers pertaining to the information contained on this wiki page are listed here.
The Board
Board Availability
- Check the DIYC Forum for the latest information concerning board availability.
Circuit Diagram
- The schematic diagram can be found here.
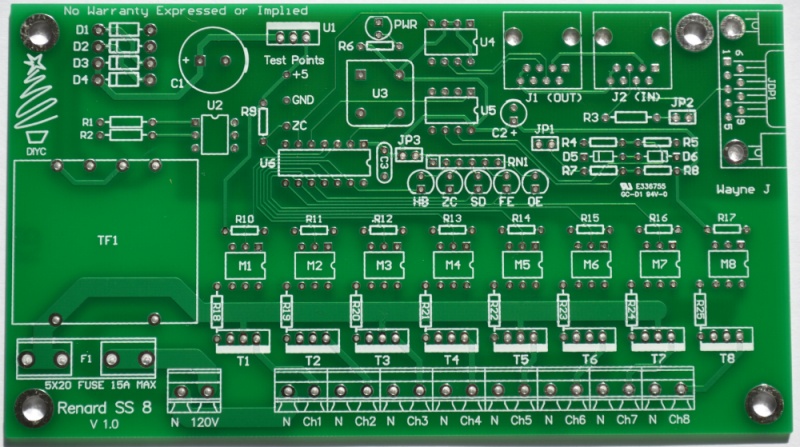
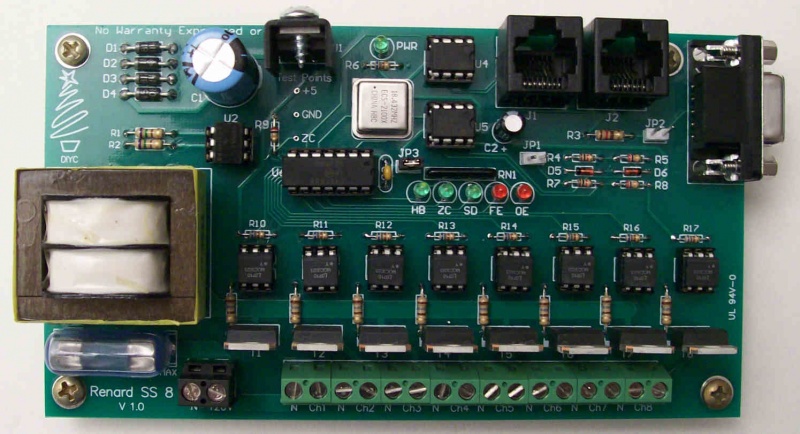
- Key circuit components
- Connectors
- J1 – RS485 outgoing data
- J2 – RS232/RS485 incoming data
- JDP1 – RS232 incoming data, DE9 connector for direct connect to show computer serial port.
- Connectors
- IC Chips
- U2 – H11AA1 Optocoupler, used to generate the Zero Cross signal
- U4 & U5 – ST485BN, RS232/RS485 Transmitter/ Receiver
- U6 – PIC16F688 Microcontroller
- M1-M8 – MOC3023 Optoisolator, triggers the triac
- IC Chips
- Resistors
- R18-25 – Triac gate resistors. The value of these resistors in the BOM was selected for locations using 115/120 VAC power.
- Resistors
- Diagnostic LEDs
- PWR – Lit whenever the voltage regulator is generating 5 VDC.
- Diagnostic LEDs
- NOTE: The following Diagnostic LEDs will only function when a jumper is placed on JP3
- When U6 is programmed with the diagnostics firmware:
- HB - will blink ON/OFF to indicate that the PIC is operating correctly
- ZC - will blink ON/OFF to indicate that the Zero Cross signal is getting to the PIC correctly
- SD - will be ON whenever the PIC is receiving data correctly
- FE - will only be ON when the PIC has identified a Framing Error while receiving data
- OE - will only be ON when the PIC has identified an Overrun Error while receiving data
- When U6 is programmed with the operational firmware:
- HB - will be ON whenever channel 2 is ON
- ZC - will be ON whenever channel 5 is ON
- SD - will be ON whenever channel 6 is ON
- FE - will be ON whenever channel 7 is ON
- OE - will be ON whenever channel 8 is ON
- Other Components
- U1 – LF50CV, 5 VDC Voltage Regulator
- U3 – ECS-2100AX-18.432MHZ, 18.432 MHz Crystal Clock Oscillator
- T1-T8 – BTA04-700T, these are gate sensitive triacs that only require 5mA of current on the gate signal. They were selected as a dual use triac for both LEDs and regular incandescent lights.
- Other Components
- Jumpers
- JP1 – RS232 signal ground. Install a shunt (jumper) on JP1 when receiving RS232 data.
- JP2 – 120 ohm termination resistor enable. Normally a shunt will be installed on JP2 when receiving RS485 data. Remove the shunt if you are experiencing problems with incoming data.
- JP3 – Diagnostic LEDs enable. Install a shunt on JP3 to allow the Diagnostic LEDs to function. During normal operation, you can remove the shunt with no negative impact on board operation.
- Jumpers
- Test Points
- +5 – Output from voltage regulator, should be +5 ± 0.1 VDC
- GND – Ground
- ZC – Zero Cross signal
- Test Points
Firmware
- The PIC (U6) must be programmed with the latest firmware for the Renard SS8 to operate properly. The firmware can be found on the Renard Firmware wiki page.
Powering the Renard SS8
- Input power requirements: An AC source
DC power:
- The Renard SS8 generates all the DC voltage that it requires on-board and no external DC voltage source is required.
AC Power:
- The Renard SS8 requires AC power for generation of the DC voltage, the SSR (opto/triac) circuitry and for generation of the Zero Cross signal. The information in this wiki is targeted at users who are using 115/120 VAC power.
AC Power Handling Capability
Maximum Input Load
- The Renard SS8 has one bank of eight triacs. This bank of triacs is capable of carrying up to 15 amps of current based on the trace width used on the pcb.
Triac Loads
- Based on the pcb trace widths, each triac can handle up to two amps of current. A heat sink is highly recommended when running the triacs at two amps. Care must be taken to ensure that the total load of the eight triacs does not exceed the rating of the fuse protecting the triac bank or 15 amps (whichever is less).
Fuses
- The bank of triacs is protected by a fuse. The size of the fuse cannot exceed the current handling capability of the input wire or 15 amps (whichever is less).
- The BOM calls for a 10 amp fuse under that assumption that the Renard SS8 will be powered by a common/generic extension cord. Most of the common extension cords used by DIYC members are rated for only 13 amps and 13 amp fuses are not commonly found.
Hooking Up the Renard SS8
Data Connections
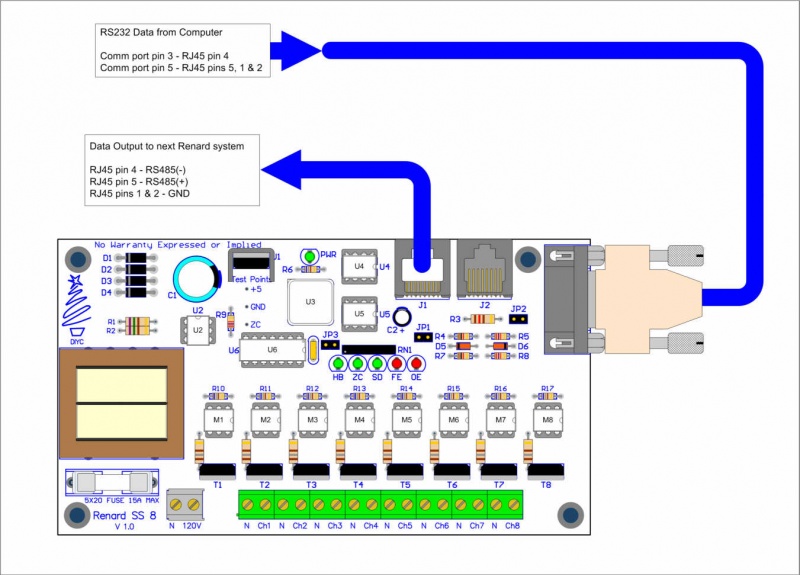
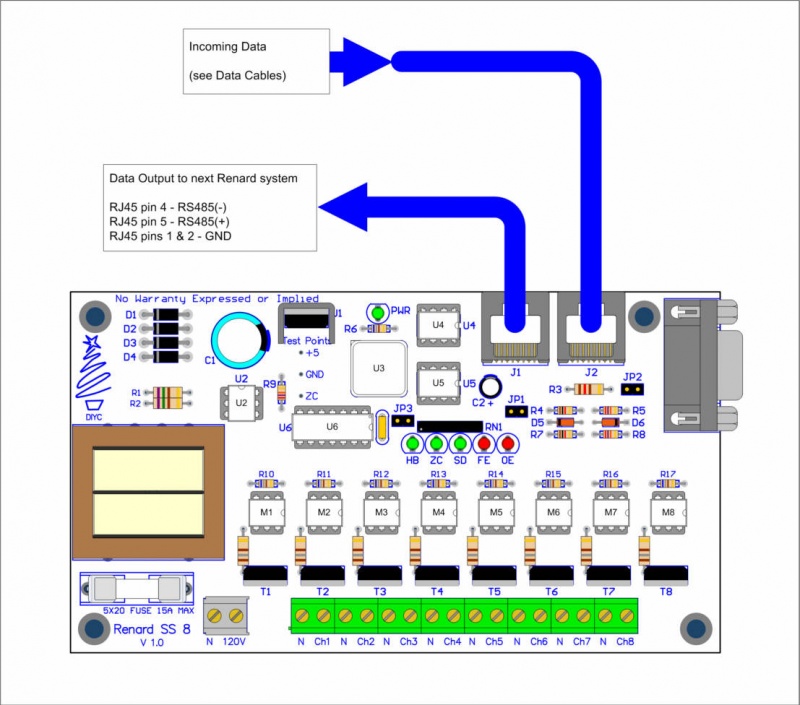
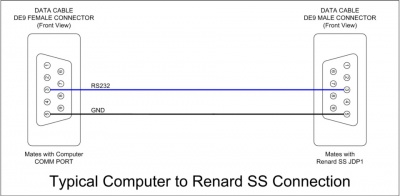
Data Cables
- Data cables for Renard SS board hookup directly to computer COMM port
PC DE9 Pin 3 to Renard SS DE9 Pin 3 PC DE9 Pin 5 to Renard SS DE9 Pin 5
PC DE9 Pin 3 to RJ45-pin 4 PC DE9 Pin 5 to RJ45-pin 5 and pin 1 and/or pin 2
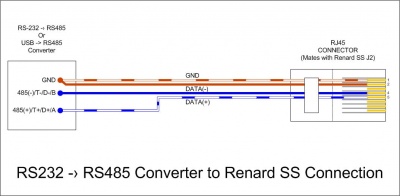
- Data cable for Renard SS board hookup using a RS232->RS485 or a USB->RS485 converter
- Due to the many different types of RS232->RS485 and USB->RS485 converters available, the drawing only refers to the signals coming from the converter. Check the documentation for your converter to figure out how/where to hook up the correct wires.
Converter signal RS485(-)/T-/D-/B/485- connects to RJ45-pin 4 (blue CAT5 wire) Converter signal RS485(+)/T+/D+/A/485+ connects to RJ45-pin 5 (blue/white CAT5 wire) Converter GND signal connects to RJ45-pins 1 & 2 (orange and orange/white CAT5 wires)
An example is shown here with the HXSP-2108F Adapter Hook-up
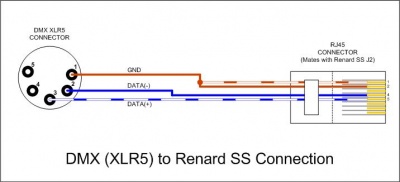
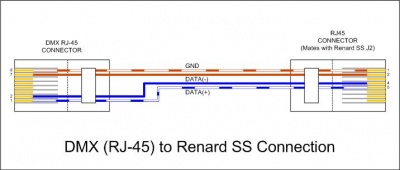
- Data cable for Renard SS board hookup in a DMX environment
DMX using XLR Connectors XLR connector pin 1 (GND) to RJ45-pin 1 and/or pin 2 XLR connector pin 2 (Data-) to RJ45-pin 4 XLR connector pin 3 (Data+) to RJ45-pin 5 DMX using RJ45 (CAT5) Connectors RJ45 connector pin 1 (Data+) to RJ45-pin 5 RJ45 connector pin 2 (Data-) to RJ45-pin 4 RJ45 connector pins 7 & 8 (GND) to RJ45-pins 1 & 2
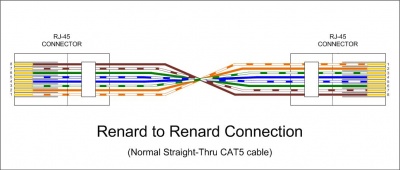
- Data cable for Renard SS board hookup to other Renard boards
Generally only a regular straight-thru CAT5 cable is required to connect Renard SS boards to other Renard boards. For the few exceptions (ie Ren24 V2.5), check the wiki page for those boards to see what their unique requirements are.
Cable Lengths
- Data cables connecting the Renard SS boards directly to a computer COMM port should not be longer than 50 feet according to the RS-232 standard. This distance can also be greatly reduced by using poor quality cables.
- Data cables connecting the Renard SS boards directly to other Renard boards or any other RS-485 source can be up to 4,000 feet in length for data rates up to 100Kbps according to the RS-485 standard.
AC Power Connection
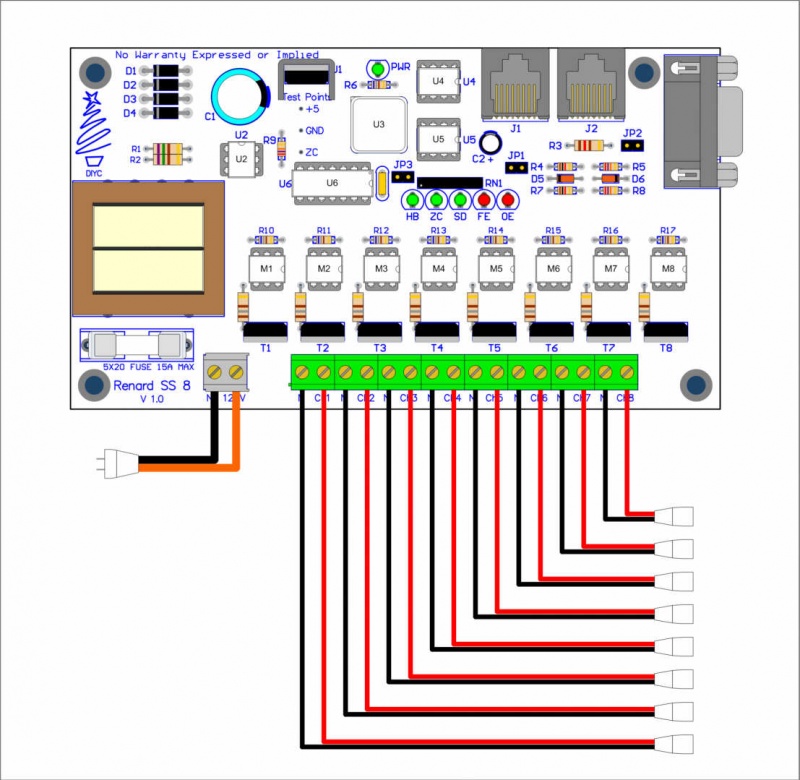
- Key thing to remember in this layout is:
- The size of the fuse cannot exceed the current handling capability of the orange/black wires or 15 amps (whichever is less).
Connecting Multiple Renard Boards
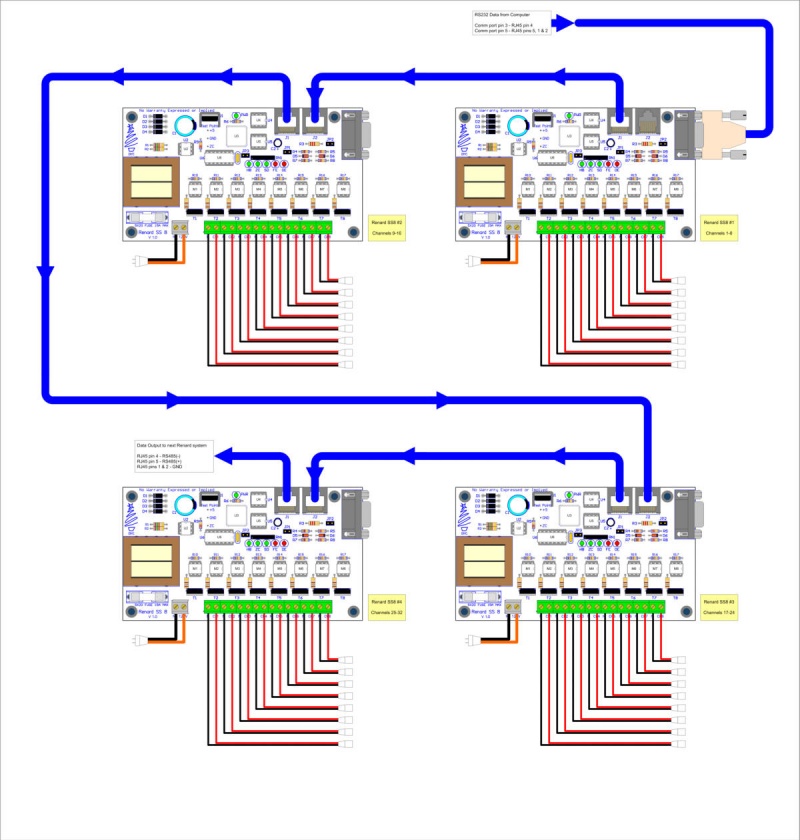
- The above image shows how Renard SS boards can be daisy chained together. Renard SS8 boards are used in the image just as an example of how all Renard SS boards can be connected together.
- Key things to remember when connecting Renard SS boards together:
- You only need one instance of the Renard Dimmer plug-in in Vixen for each physical COMM port being used. You just need to make sure that the plug-in is setup for the total number of channels for all the Renard boards connected to that COMM port. In the above example, the plug-in would be set for 32 channels.
- The total number of Renard boards that can be connected together depends on the event period and the baud rate being used. More information on the total number of channels capable with Renard systems can be found here here.
Configuring the jumpers on Renard SS boards
- JP1 & JP2 Configuraton
- The configuration of JP1 and JP2 depends on the type of communication being used:
- RS-232 Communication (direct connect to PC)
- JP1 installed
- JP2 not installed
- RS-232 Communication (direct connect to PC)
- Reminder: This only applies to the first Renard SS board connected to the PC. The output of a Renard SS board to the next board is RS-485.
- RS-485 Communication (output of a Renard board or output from a RS-485 adapter/converter)
- JP1 not installed
- JP2 installed (try removing if data communication issues are encountered)
- RS-485 Communication (output of a Renard board or output from a RS-485 adapter/converter)
- JP3 Configuraton
- Installed when running the Diagnostics Firmware
- Normally not installed when running the Operational Firmware. But can be left installed if you don’t mind seeing the on-board LEDs responding with the associated channels.
Computer Setup
- VIXEN Settings
- The Renard SS boards require the Renard Dimmer [Vixen 1.1.*] or Renard Dimmer (modified) [Vixen 2.*] Plug-In.
- Renard Dimmer Plug-In Settings:
- Protocol Version: 1
- COM1 (or whichever COM port you are connected to)
- Baud: 57600 (default firmware value, if firmware is changed then this needs to be changed to match the firmware)
- Parity: None
- Data bits: 8
- Stop bits: One
- Hold port open during the duration of the sequence execution: Checked
- Renard Dimmer Plug-In Settings:
Setup for Beginners and Troubleshooting
- If you are unsure that you have built your hardware correctly, you should follow the procedures contained in the Renard SS8 Beginners Setup Guide. These procedures will guide you through the steps to help setup the hardware for the first time.
- If you encounter any problems with your Renard SS8, you can go to the Troubleshooting Guide The Renard SS8. The troubleshooting guide contains a methodical process to try to isolate problems/malfunctions and gives suggestions of what to do to fix them.